what is the difference between machine learning and deep learning
Machine learning and deep learning are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they refer to two distinct types of artificial intelligence. Both machine learning and deep learning are used to enable machines to learn and make decisions on their own, but there are some fundamental differences between the two.
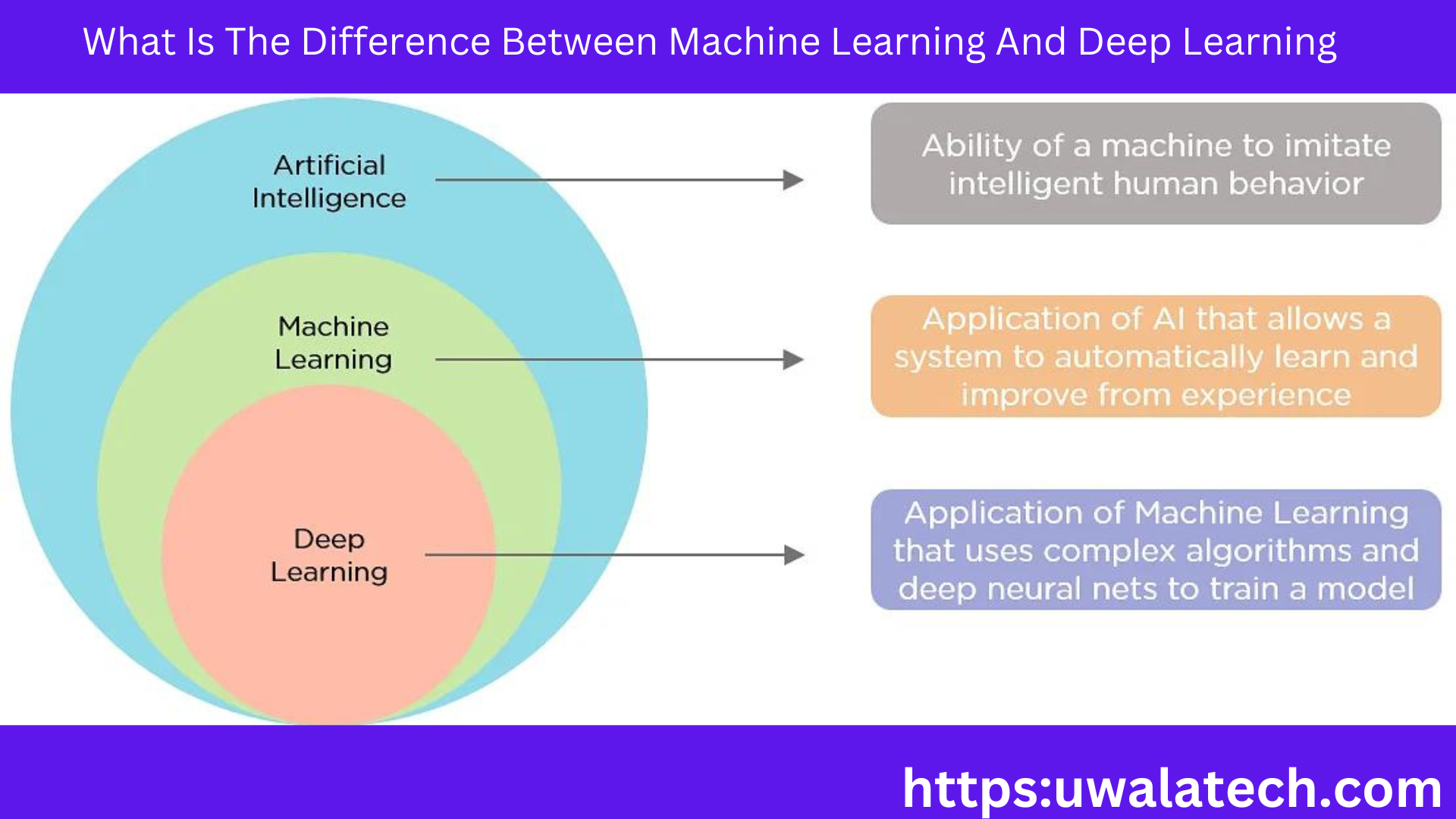
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on enabling machines to learn and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms use statistical models to learn from data and make predictions or decisions based on that data.
The primary goal of machine learning is to find patterns in data and use those patterns to make predictions or take actions. For example, machine learning algorithms can be used to predict stock prices, recommend products to customers, or detect credit card fraud.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on using neural networks to learn from data. Neural networks are a set of algorithms that are modeled after the structure and function of the human brain.
Deep learning algorithms are designed to learn from large amounts of data by processing it through layers of neural networks. Each layer in the network processes the data and passes it on to the next layer, gradually building a more complex understanding of the data.
The primary goal of deep learning is to enable machines to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence, such as image recognition, speech recognition, and natural language processing.
Key Differences between Machine Learning and Deep Learning:
Data Requirements:
- Machine learning algorithms can learn from smaller datasets and do not require large amounts of data. On the other hand, deep learning algorithms require vast amounts of data to train and perform well.
Model Complexity:
- Machine learning models are generally simpler and require less computational power than deep learning models, which are highly complex and require massive amounts of computational power.
Feature Engineering:
- In machine learning, feature engineering is the process of selecting and extracting relevant features from the data to train the model. In deep learning, feature engineering is often unnecessary as the algorithms can learn the relevant features on their own.
Interpretability:
- Machine learning models are generally easier to interpret than deep learning models, which are often considered “black boxes” due to their complex structure.
Conclusion:
In summary, machine learning and deep learning are both subsets of artificial intelligence that are used to enable machines to learn from data and make decisions. The primary difference between the two is that machine learning is focused on finding patterns in data and making predictions, while deep learning is focused on enabling machines to perform tasks that require human-like intelligence. Understanding the differences between machine learning and deep learning can help organizations choose the best approach for their specific needs.